OpenAI
This page provides information for connecting Appsmith to OpenAI, which allows you to configure applications with advanced AI capabilities such as natural language processing and image analysis.
Connect OpenAI
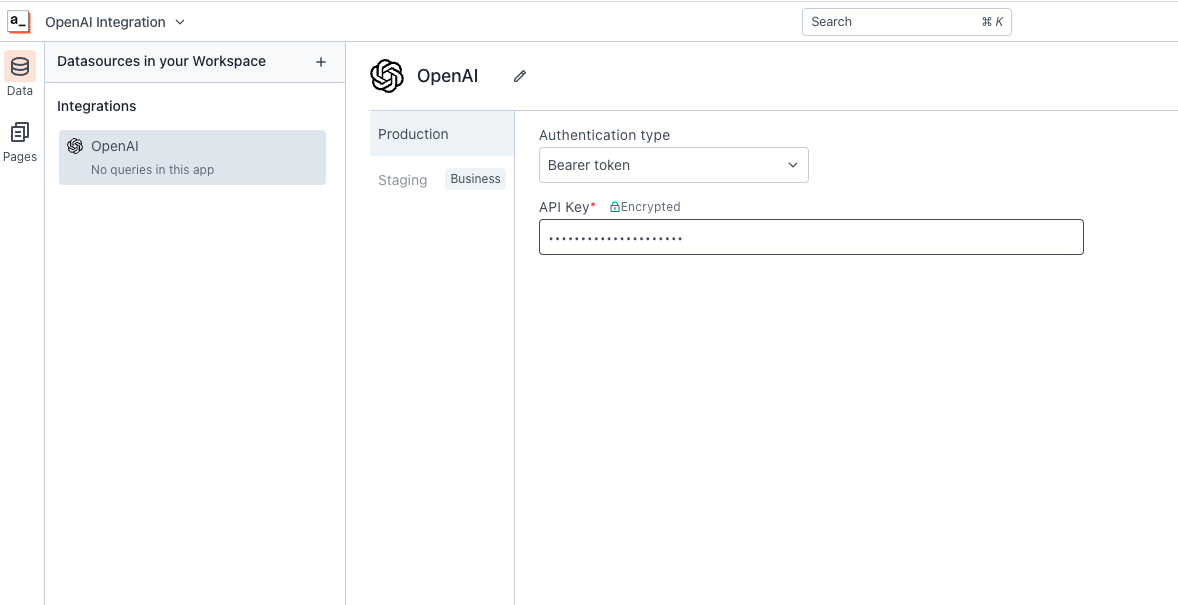
Connection parameters
The following section is a reference guide that provides a complete description of all the parameters to connect to a OpenAI datasource.
Authentication type
Authentication Type refers to the method used to verify the identity of users or systems interacting with the OpenAI API.
Options:
- Bearer Token: It is a type of access token that is included in the request headers to authenticate and authorize API requests.
API Key
The OpenAI uses API keys for authentication. Visit the API Keys page to retrieve the API key.
Query OpenAI
The following section is a reference guide that provides a description of the available commands with their parameters to create OpenAI queries.
Chat
The Chat command generates human-like text based on input prompts. The following section lists all the available parameters:
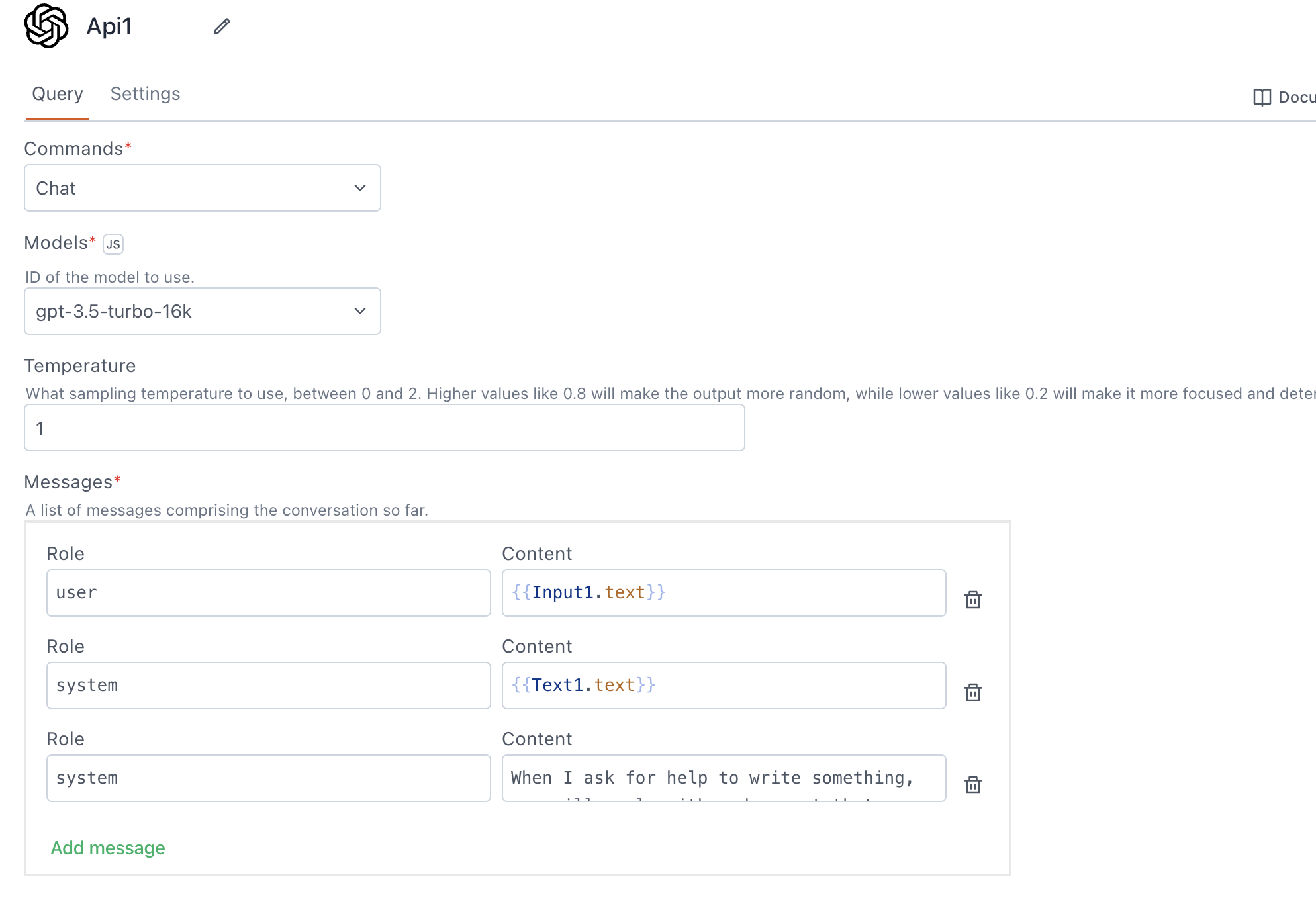
Models
It refers to the pre-trained language models provided by OpenAI. You can select from the available list of models, including options like GPT-3, GPT-4, and others.
Temperature
Temperature determines the level of randomness in the output. It ranges between 0 and 2.
Lower values for temperature result in more consistent outputs (e.g. 0.2), while higher values generate more diverse and creative results (e.g. 1.0). Select a temperature value based on the desired trade-off between coherence and creativity for your specific application.
Messages
Messages serve as input interactions between the user and the model. You can create multiple messages of each type to make your conversation just the way you want. In the Roles parameter, you can specify either user or system. In the Content property, add:
- system: The system message serves as a means to provide additional context, set guidelines, or convey the overall objective of the task. It helps shape the behavior of the model's responses. For example, you can use the system message to give personality to the responses or add task-specific instructions. For example, you can set system as:
"You are a technical support assistant. Provide clear and detailed solutions to user queries related to software issues. If the user mentions a bug, ask for additional details to troubleshoot effectively."
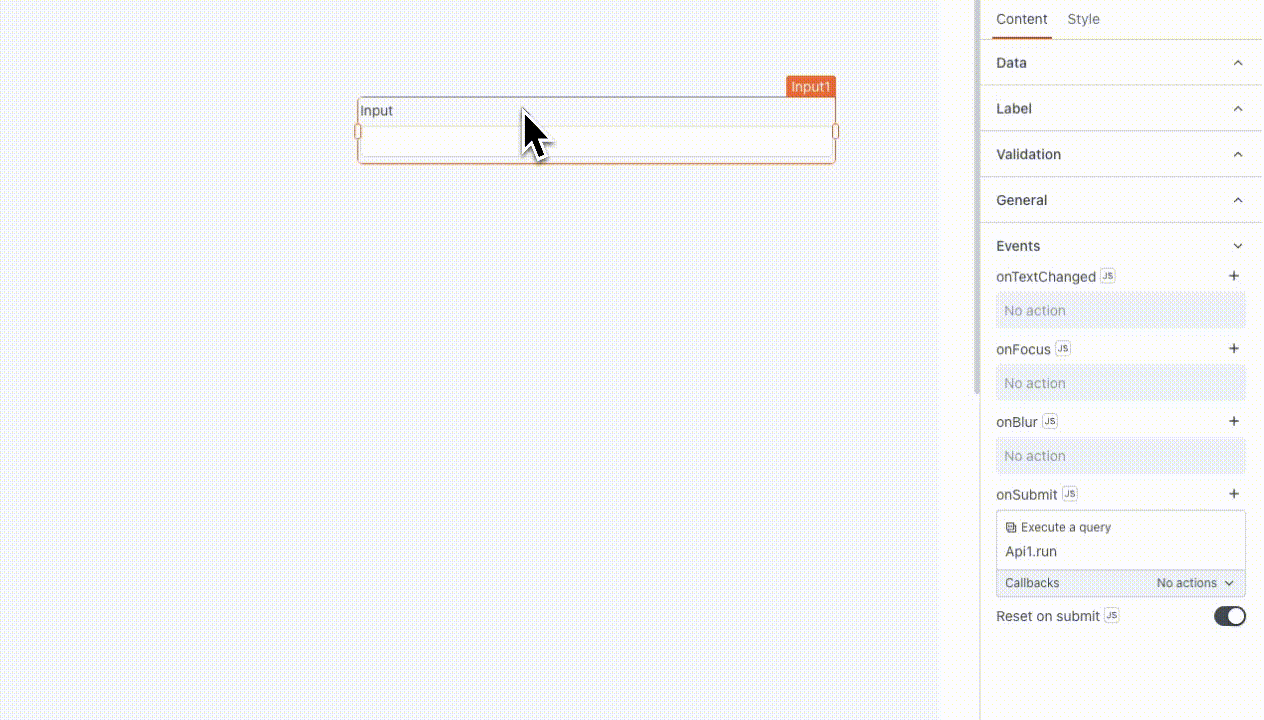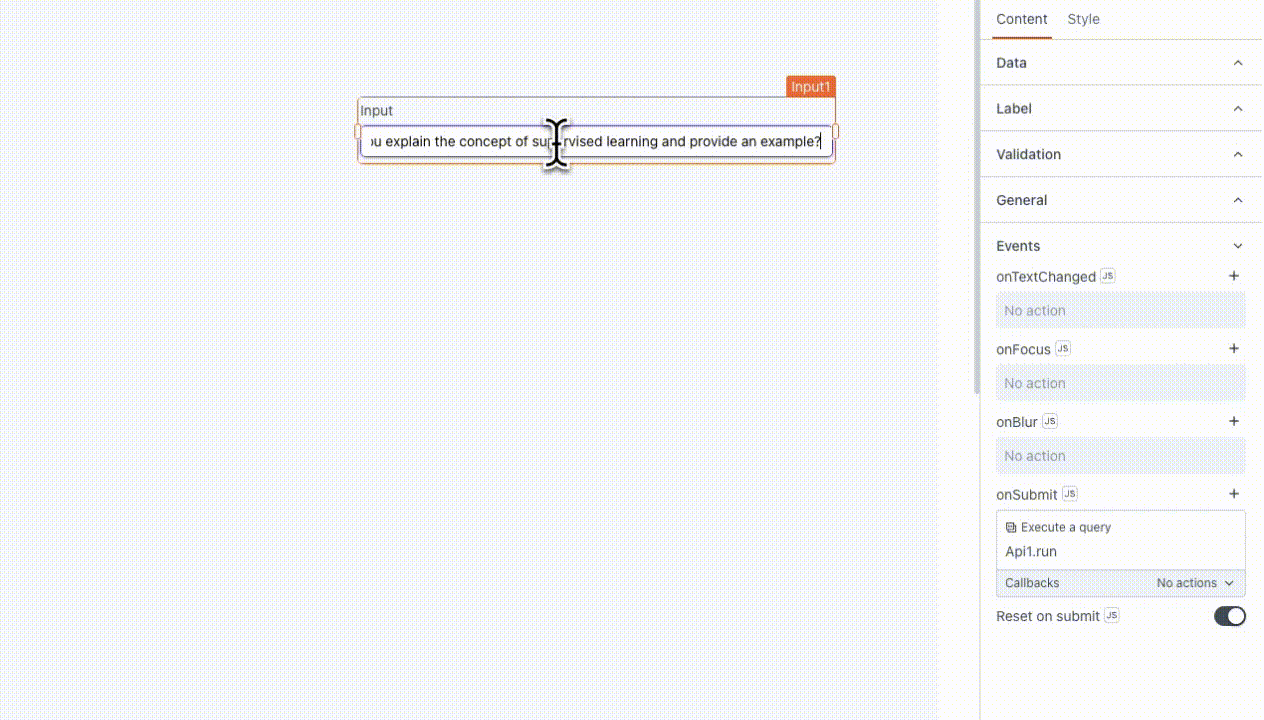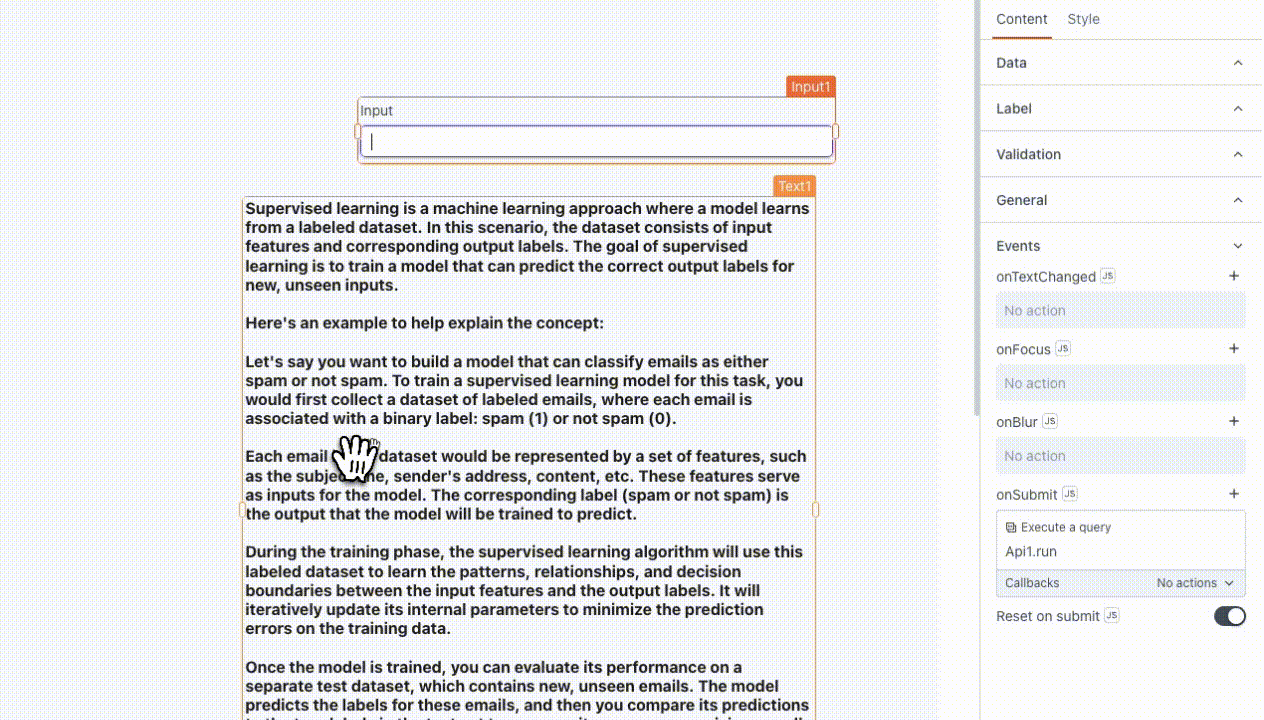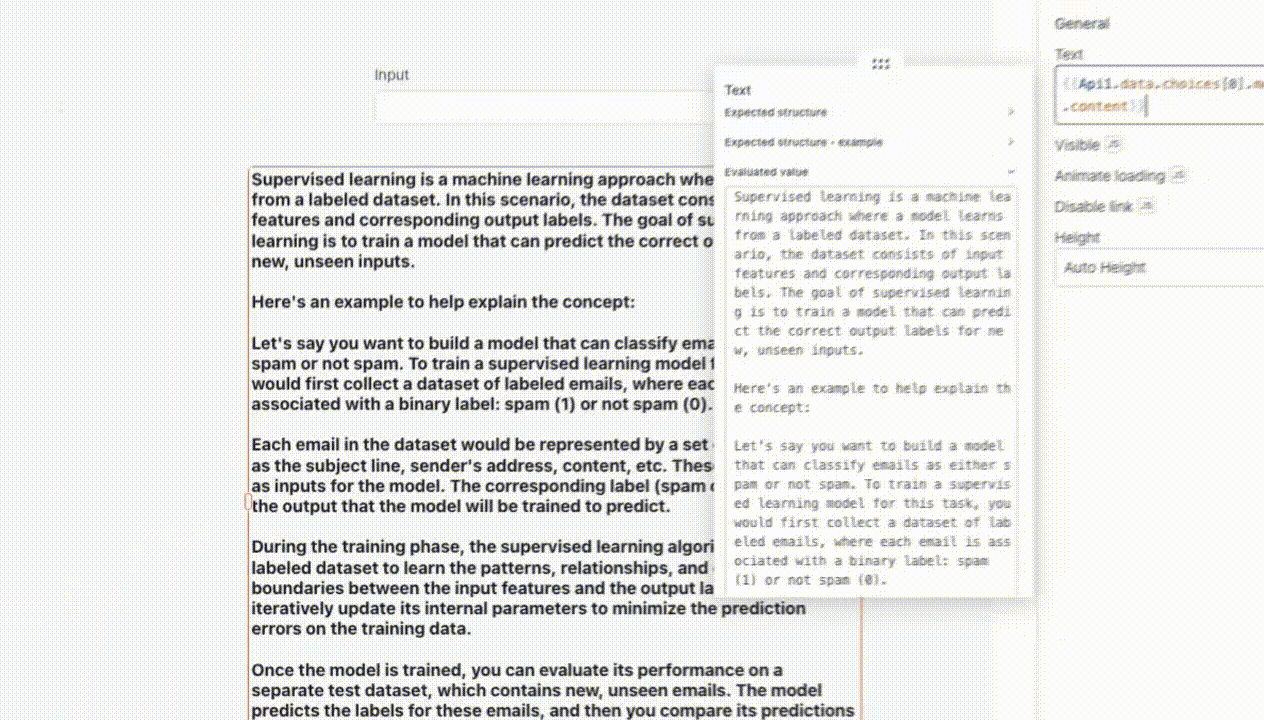
- user: Input provided by the user to instruct or guide the model. For example, if you are using an Input widget to enter the prompt, you can use
{{Input1.text}}.
For more information refer to the OpenAI documentation.
Embeddings
The Embeddings command creates a vector representation of a given input, making it easier to perform tasks like semantic search or text similarity.
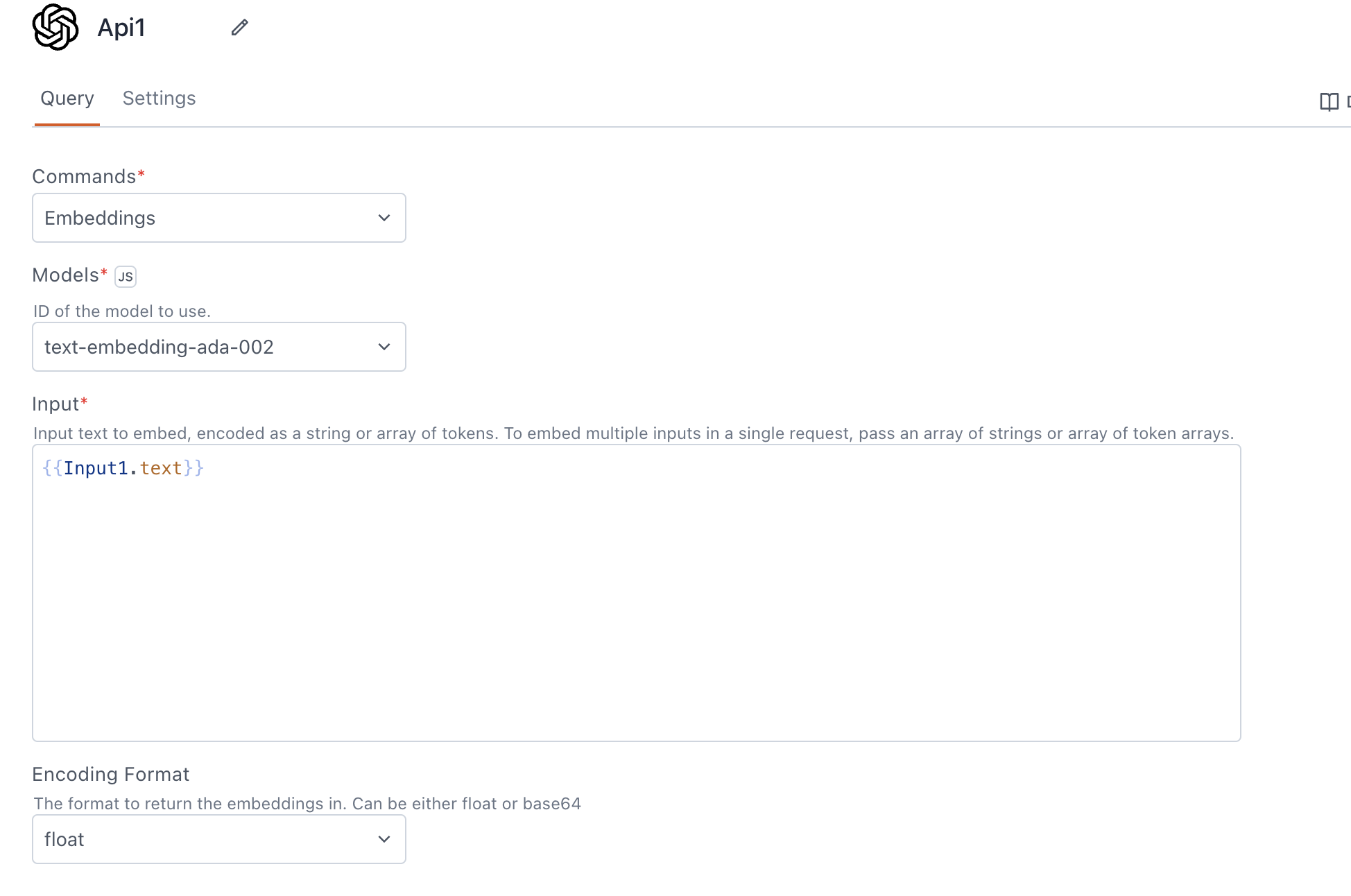
Models
Models are pre-trained language models provided by OpenAI. You can select from the available list of models, like text-embedding-ada-002.
Input
Input text to embed, encoded as a string or array of tokens. To embed multiple inputs in a single request, pass an array of strings or array of token arrays. You can add text information using either the Rich Text Editor or Filepicker widget, and store it in a vector database for subsequent similarity searches.
Encoding format
The encoding format determines how the embeddings are returned.
Options:
- Float: Returns the embeddings in float format.
- Base64: Returns the embeddings encoded in Base64 format.
While it is technically possible to bind the output of the embeddings API to a widget, doing so offers little practical value, as the vector representation is not meaningful for direct display in the UI. Instead, you can store it in a specialized database called a Vector DB. Later, you can leverage these vectors for semantic search operations to retrieve related content based on the meaning of a query. For more information on embedding refer to the OpenAI documentation.
Vision
The Vision command allows the model to take in images and answer questions about them.
Models
Models are pre-trained vision models provided by OpenAI. You can select from the available list of models, like gpt-4-vision.
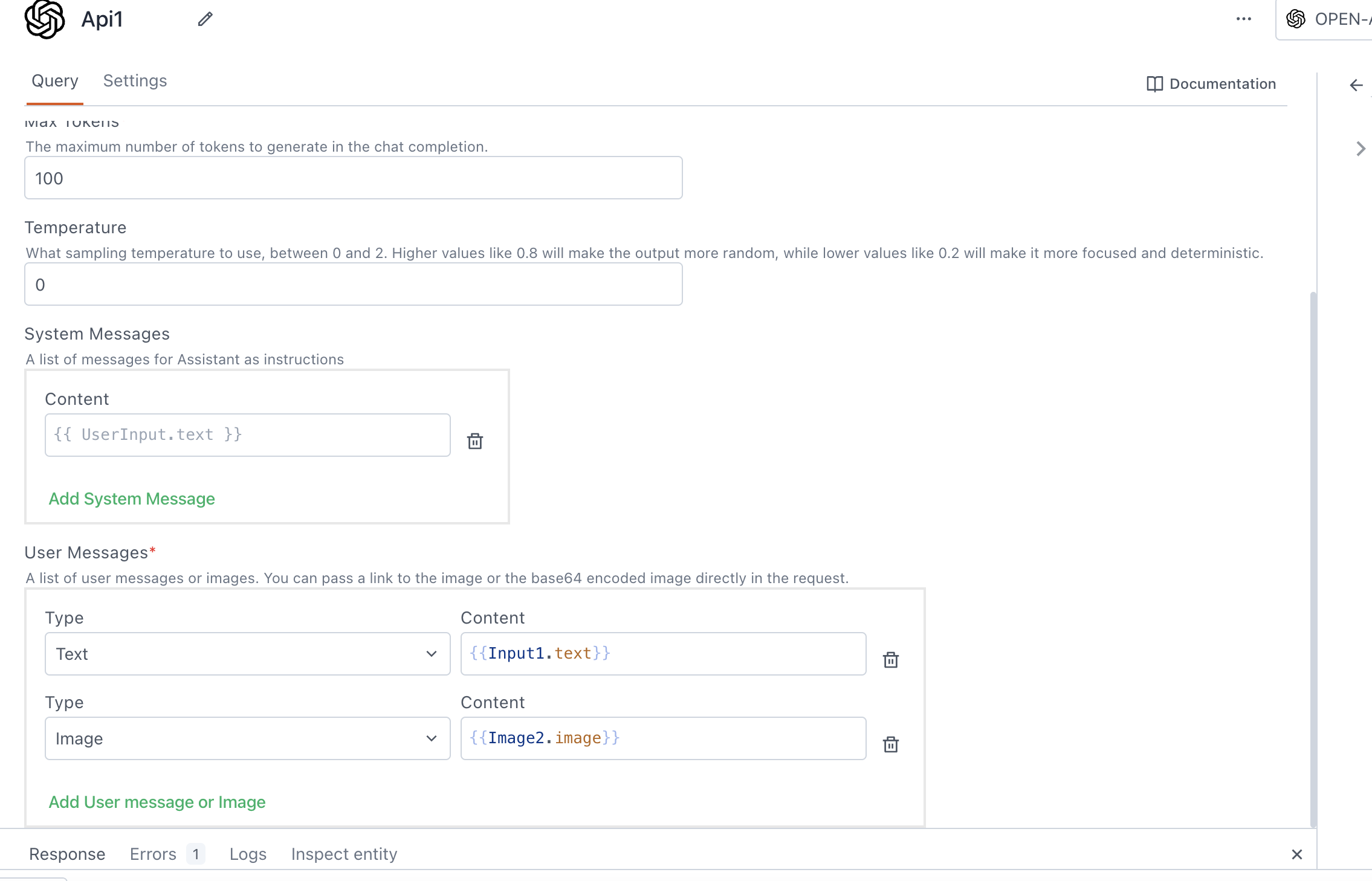
Max tokens
The maximum number of tokens the response should contain. It allows you to control the length of the generated output.
Temperature
Temperature determines the level of randomness in the output. It ranges between 0 and 2.
Lower values for temperature result in more consistent outputs (e.g. 0.2), while higher values generate more diverse and creative results (e.g. 1.0). Select a temperature value based on the desired trade-off between coherence and creativity for your specific application.
System messages
These messages help shape the behavior of the model's responses and can be used to add personality, offer instructions, or guide the model in generating more contextually relevant outputs. You can add multiple system messages as required.
User messages
User messages consist of a list of messages or images provided by the user.
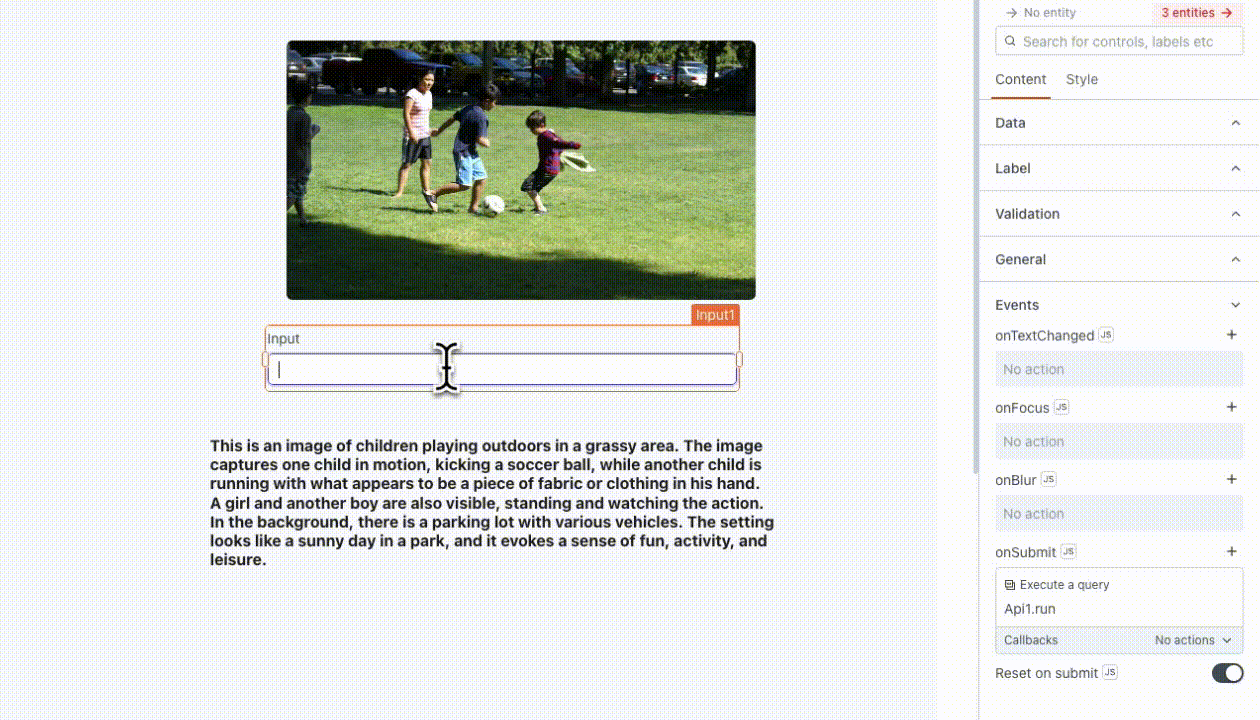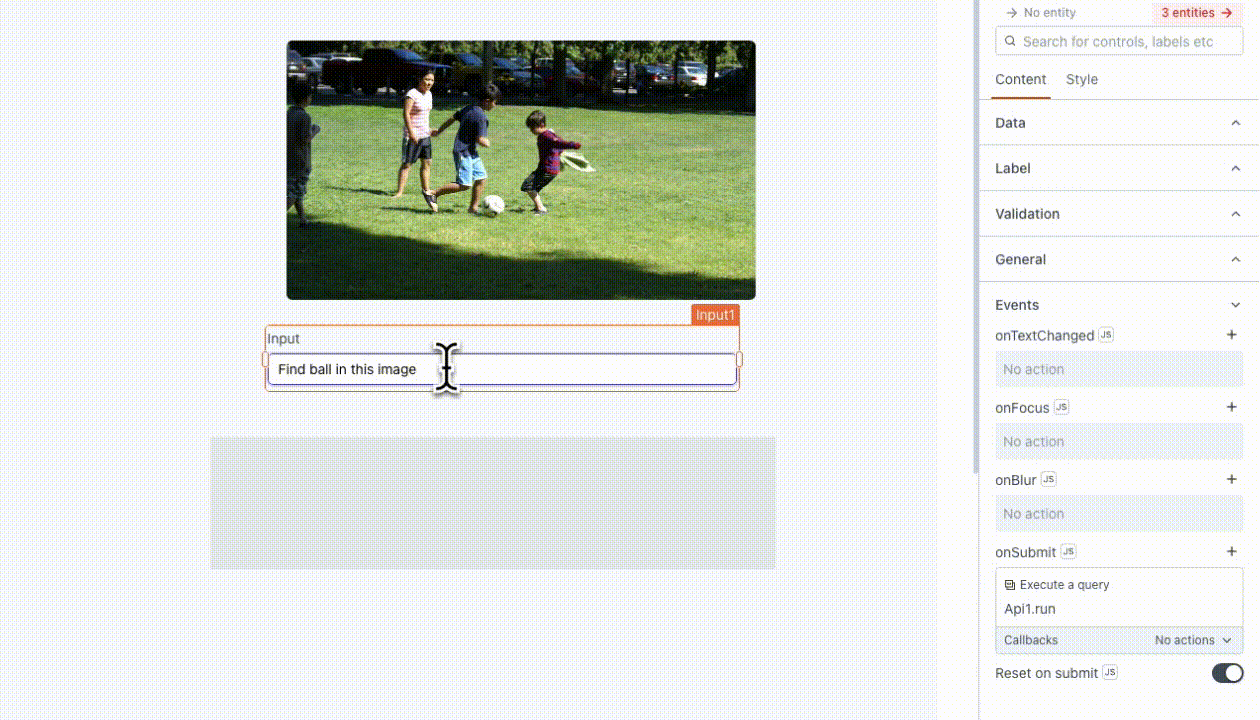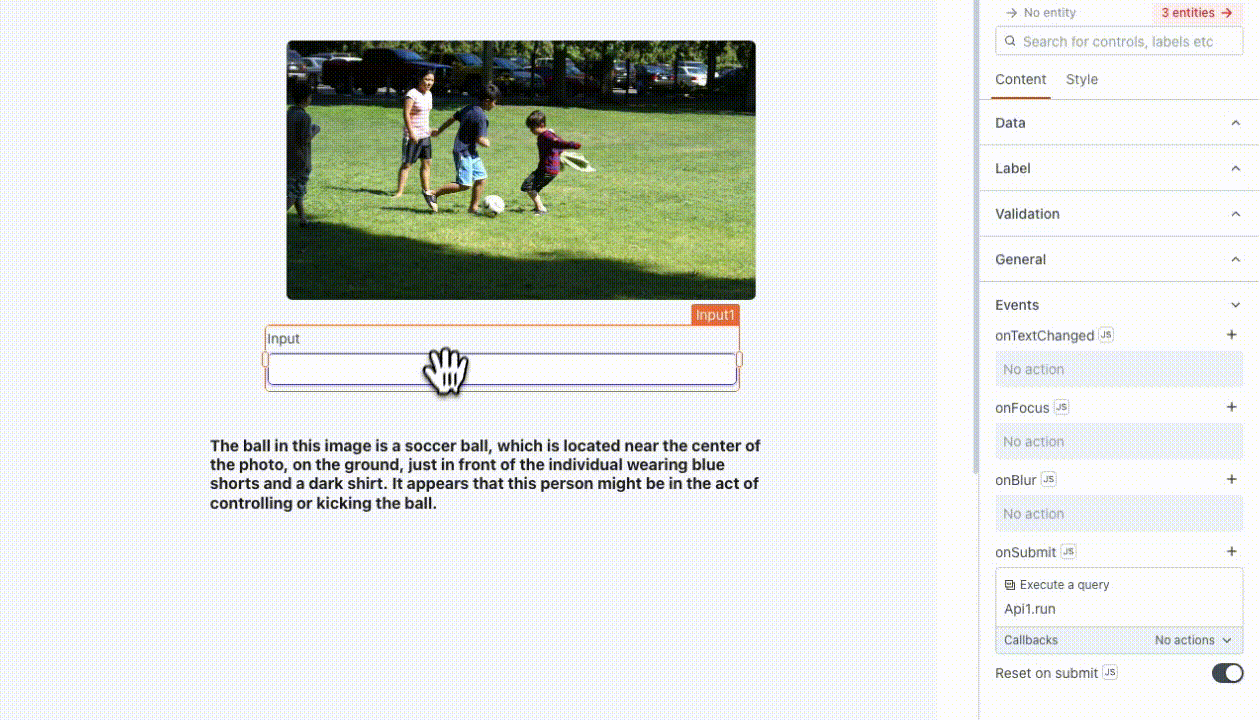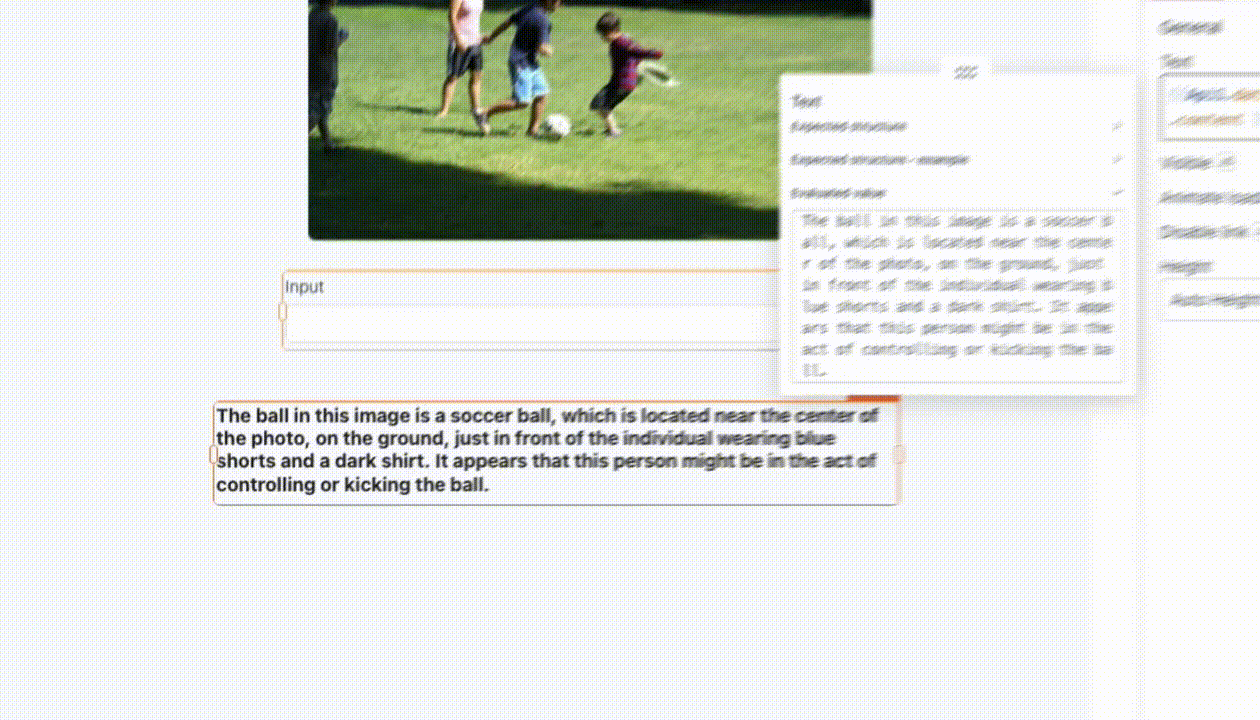
Text: This represents the task input you want to send to OpenAI. For example, you can use it to instruct the model, such as "find a ball in this image," using
{{Input1.text}}.Image: This is the image on which the model performs tasks based on the provided text. You can pass a link to the image or the base64 encoded image directly in the request. You can also add multiple images as needed. For example, you can use the Filepicker to upload images, like as
{{FilePicker1.files[0].data}}.
For more information refer to the OpenAI documentation.