Setup Branches
Similar to using Git flow in SDLC, you can make separate branches in Appsmith for different stages of your app development. It's recommended to set up the branches for the development phases as given below:
- Master - The master branch contains the final version of the app that's accessible to the app viewer. You can make this branch protected from the settings in the remote repository.
- Release - Create a new branch
releasefrom the master branch where all the feature branches should be merged. In this branch, the app goes through testing and QA. When the QA is completed, raise a PR from the release to the master branch in the remote repository. - Feature - A feature branch is for the developers to work on building the app. Each developer should have an individual feature branch and on completion, raise a PR to the release branch in the remote repository
It is recommended that each developer should have an individual feature branch.
Branch URLs
Each branch that you create has its own unique URL in the following format:
<APPSMITH-APP-URL>?branch=<BRANCH-NAME>
For instance, if you want to open your app in the release branch, replace <BRANCH-NAME> with "release" in the URL. These URLs can be shared with others to view the deployed version of the app for that branch.
In case the branch name is not mentioned in the URL, the URL directs to the default branch, which is the master branch.
Create a branch
To create these branches in your Appsmith app, follow the steps below:
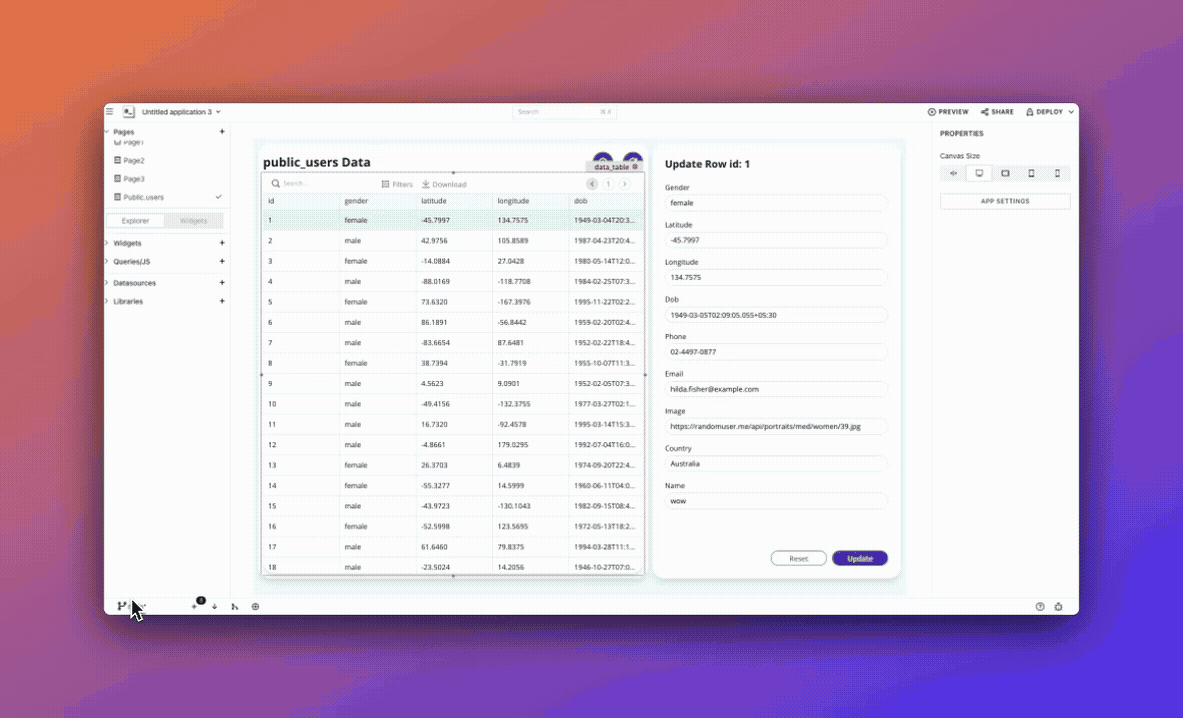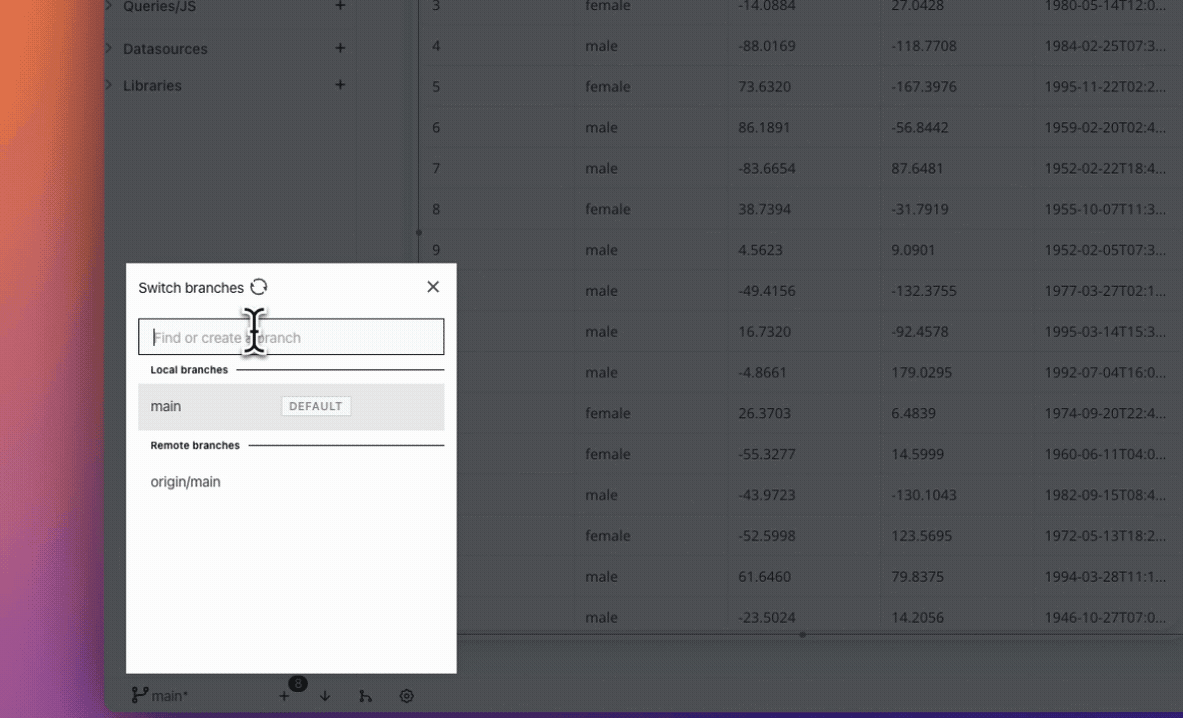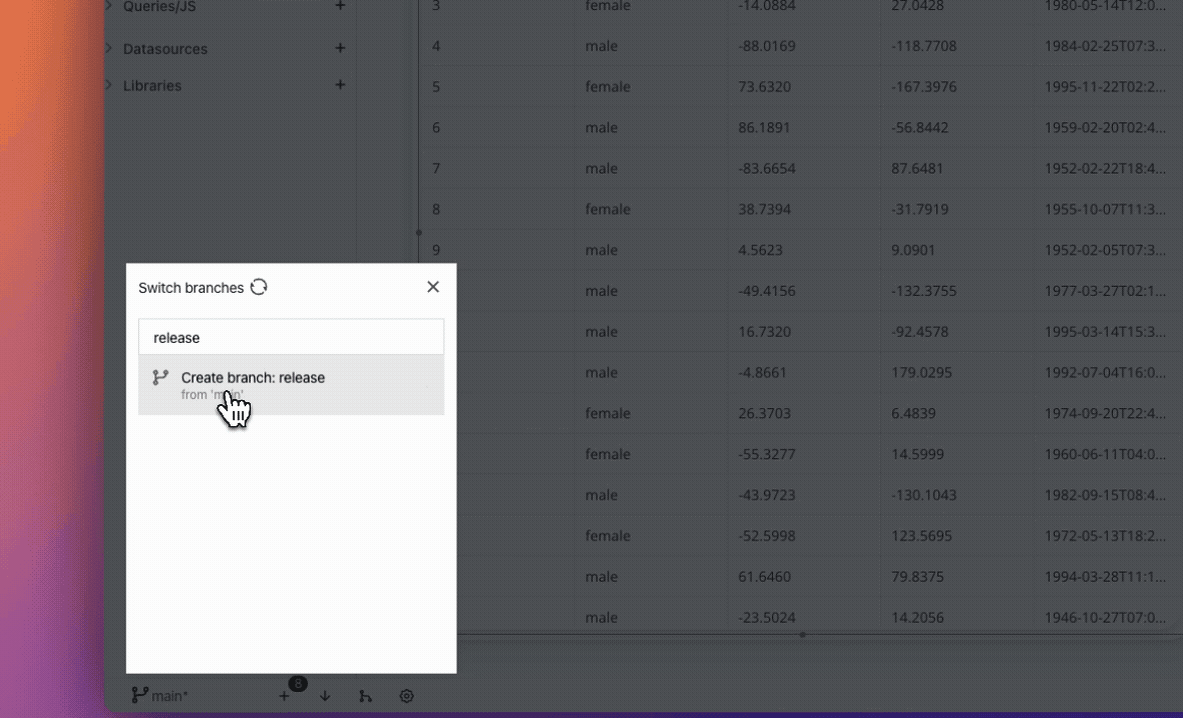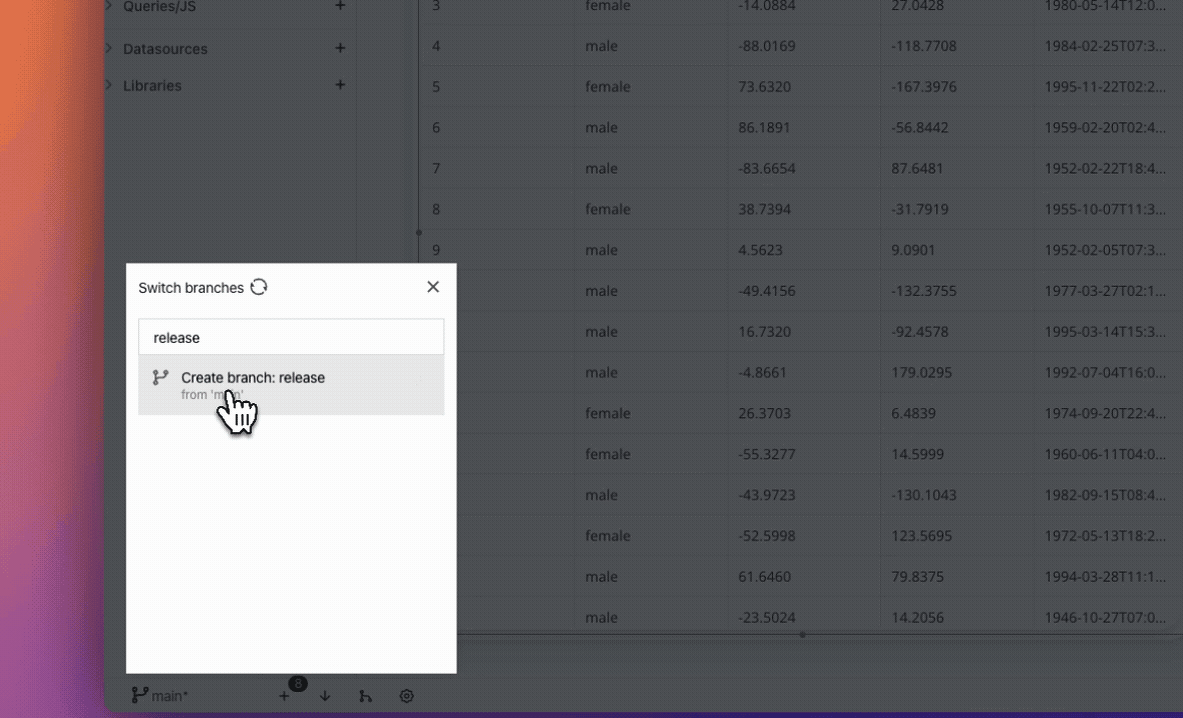
- Click the current branch at the bottom left corner to open the branch Modal that shows the list of existing branches.
- To create a new branch, enter the new branch name (Eg. release) in the input box and click on Create branch:release. Your application switches to the new (release) branch.
Please keep the following points in mind when creating a new branch:
- When you create a new branch, it includes any uncommitted changes from its parent branch.
- When you switch to another branch, any uncommitted changes in your current branch are not transferred to the destination branch.
- Attempting to check out a remote branch that already has a local version can result in an error.
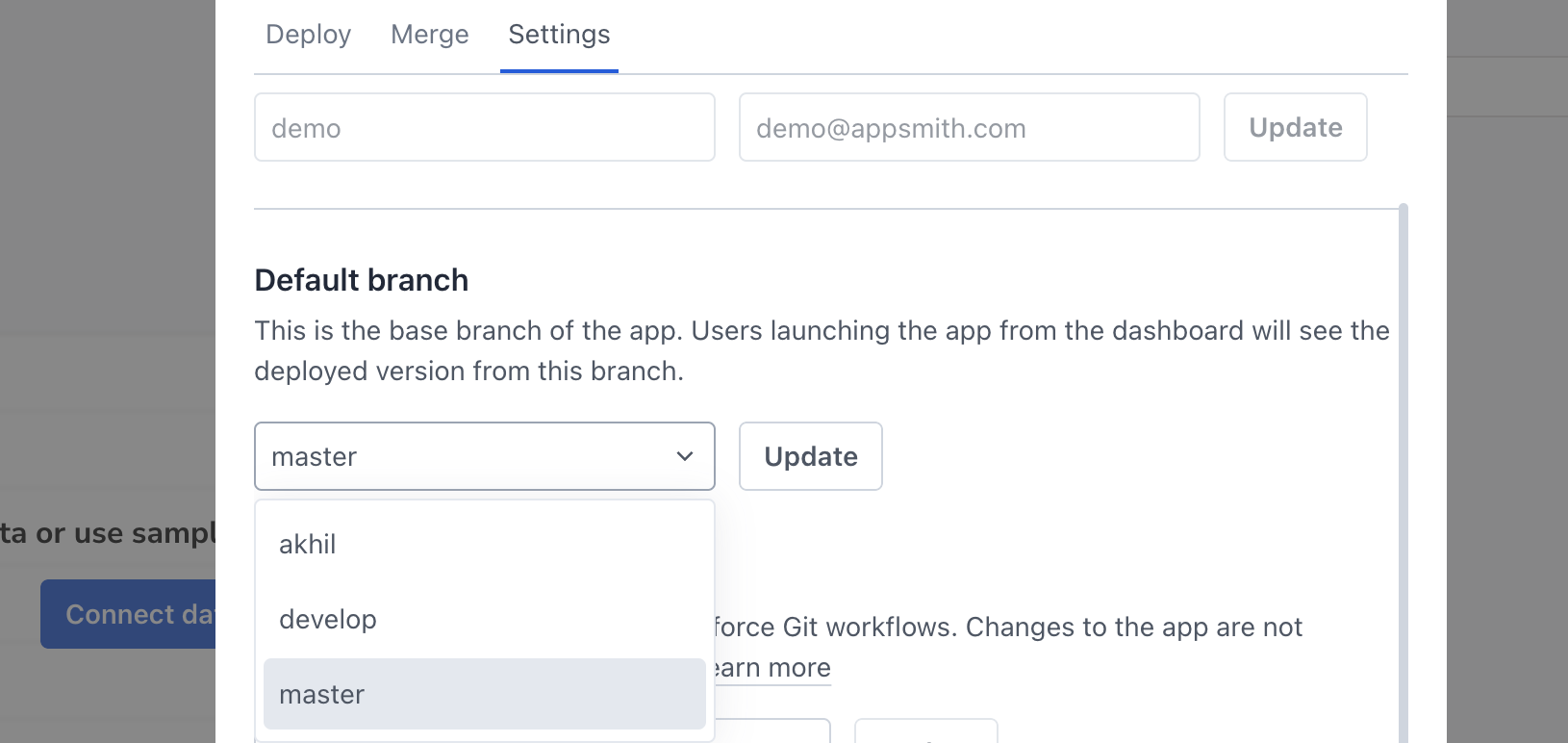
Default branch
The default branch is the base branch of the app. Users launching the app from the dashboard will see the deployed version from this branch. It is the branch where all changes are eventually merged back. It's the central hub from which new features, bug fixes, and other changes are based and into which they are integrated.
If you are an enterprise user and using Git across multiple instances, you have the option to select a different default branch for each instance, offering configuration based on specific project requirements or preferences.
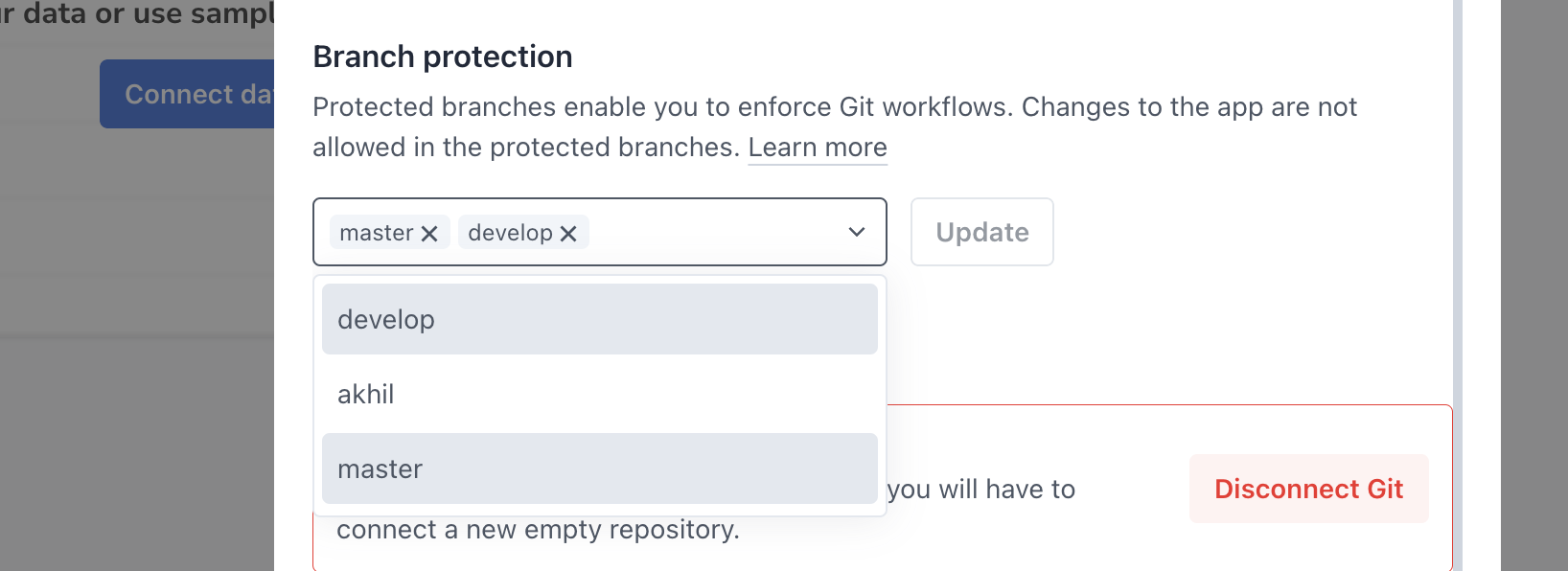
Branch protection
Changes to the app are not allowed in protected branches, the user needs to create a new branch or checkout an existing branch to edit the app. This enforces Git Workflows, ensuring development happens securely and by following good development practices.
If you are an enterprise user, you can select multiple branches as protected, enhancing security measures across various aspects of the codebase. However, for non-enterprise users, the default branch is automatically set as the protected branch. You have the option to exclude the default branch from branch protection if needed, from the Git settings located in the left corner.
Learn how to create and maintain multiple versions of your applications and make changes to them in isolation using Git.
